***
Earth Complaints


for DECADES WE DIDN'T LISTEN

for DECADES WE DIDN'T LISTEN

for DECADES WE DIDN'T LISTEN

for DECADES WE DIDN'T LISTEN
for DECADES WE DIDN'T LISTEN

for DECADES WE DON'T LISTEN

for DECADES WE DIDN'T LISTEN
DESALINATION: A SOLUTION FOR WATER SCARCITY, AGRICULTURE, AND CLEAN ENERGY
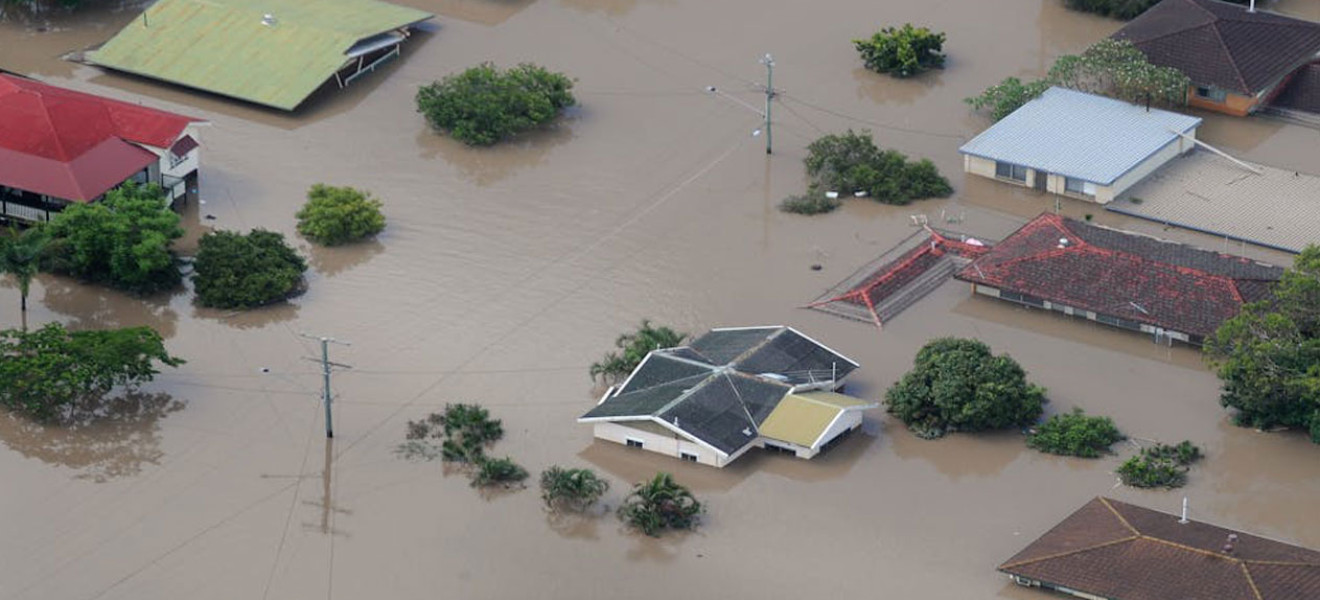
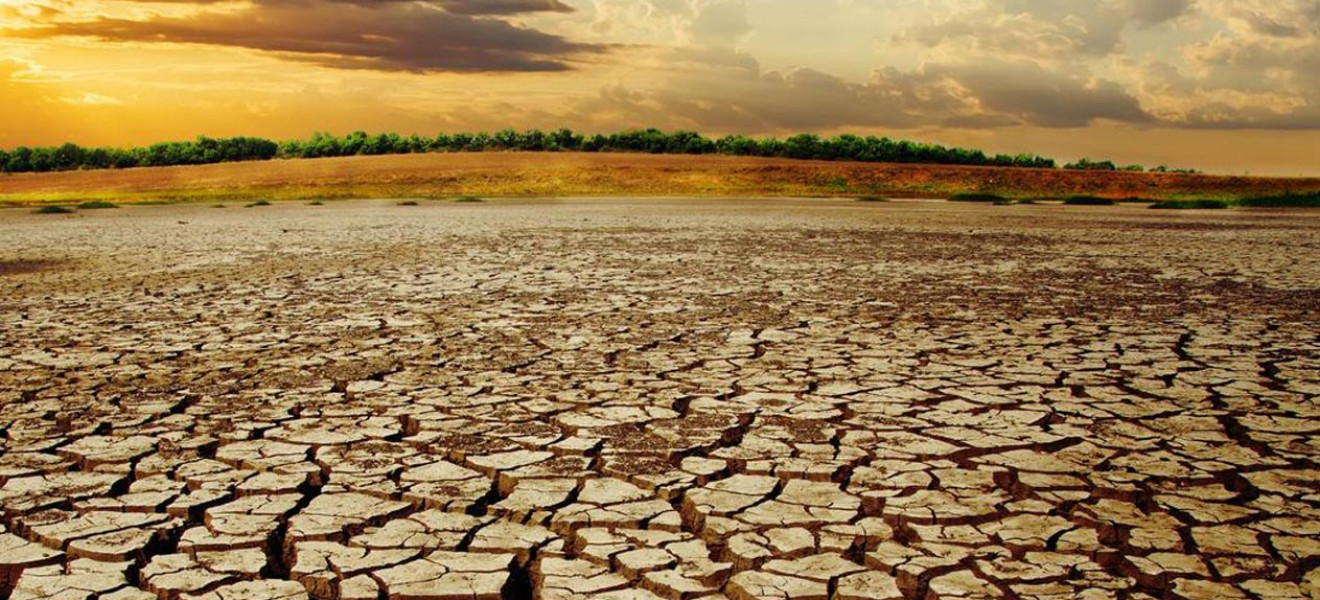
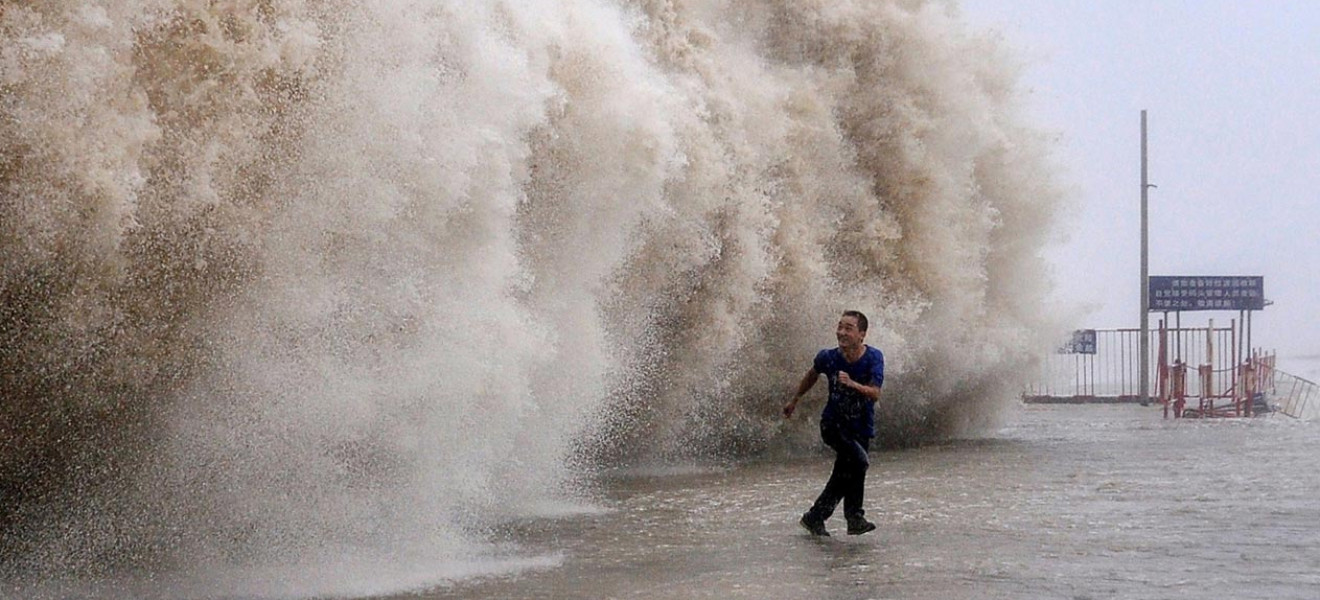
Floods and droughts are two extreme weather events that significantly impact farmland and food supplies, posing serious challenges to global food security.
Challenges ahead
Even if one doesn’t believe that climate change intensifies extreme weather events, the growing threats of floods, droughts, and rising seawater levels to livelihoods are undeniable. Addressing these challenges requires proactive measures, including building desalination plants.
These plants can provide fresh water for consumption and irrigation, helping stabilize food production during droughts. Beyond this, desalinated water mitigates rising water levels and can support PEM hydrogen production, a process that uses electrolysis to produce hydrogen, which can then be used to generate clean electricity. This dual-purpose approach not only addresses water scarcity but also contributes to sustainable energy solutions, enhancing resilience to future challenges.
FIND OUT MORE
Floods
Floods occur when excessive rainfall overwhelms natural drainage systems, rivers, or dams. These events can devastate agricultural land by:
- Erosion and Soil Degradation: Floodwaters wash away topsoil, which is rich in nutrients essential for crop growth.
- Crop Damage: Prolonged inundation can destroy crops outright, especially those not resilient to waterlogging.
- Contamination: Floodwaters often carry pollutants, such as chemicals and sewage, which can contaminate farmland and make it unsuitable for future planting.
- Disrupted Harvesting: Farmers may lose entire growing seasons, leading to shortages in local and global food supplies.
Droughts
Droughts, defined by prolonged periods of insufficient rainfall, have equally dire consequences:
- Water Scarcity: Reduced water availability limits irrigation, leading to decreased crop yields.
- Soil Degradation: Droughts can cause soil compaction and loss of organic matter, reducing land fertility.
- Crop Failures: Plants wither due to lack of water, leading to widespread harvest failures.
- Livestock Losses: Insufficient water and forage impact livestock health, reducing meat and dairy production.
WHAT CAN WE DO? FIND OUT
Impact on Farmland and Food Supplies
The combined effects of floods and droughts can create severe disruptions:
- Reduced Agricultural Output: Repeated weather extremes lower productivity, driving up food prices.
- Food Insecurity: Populations in affected regions face higher risks of malnutrition and famine.
- Economic Strain: Farming communities often struggle to recover from financial losses caused by destroyed crops and infrastructure.
- Global Ripple Effects: As major agricultural regions are impacted, the effects cascade across international food markets, exacerbating supply chain disruptions.
Long-Term Considerations
Adapting to these challenges requires integrated strategies such as improved irrigation systems, flood-resistant crops, better soil management practices, and global cooperation to address climate change. Without such measures, the frequency and intensity of these events could worsen, further endangering global food systems.

